Privacy-Preserving Machine Learning and Data Sharing in Healthcare Applications
![]() Download PDF
Download PDF
![]() Citation
Citation
![]() Google Scholar
Google Scholar
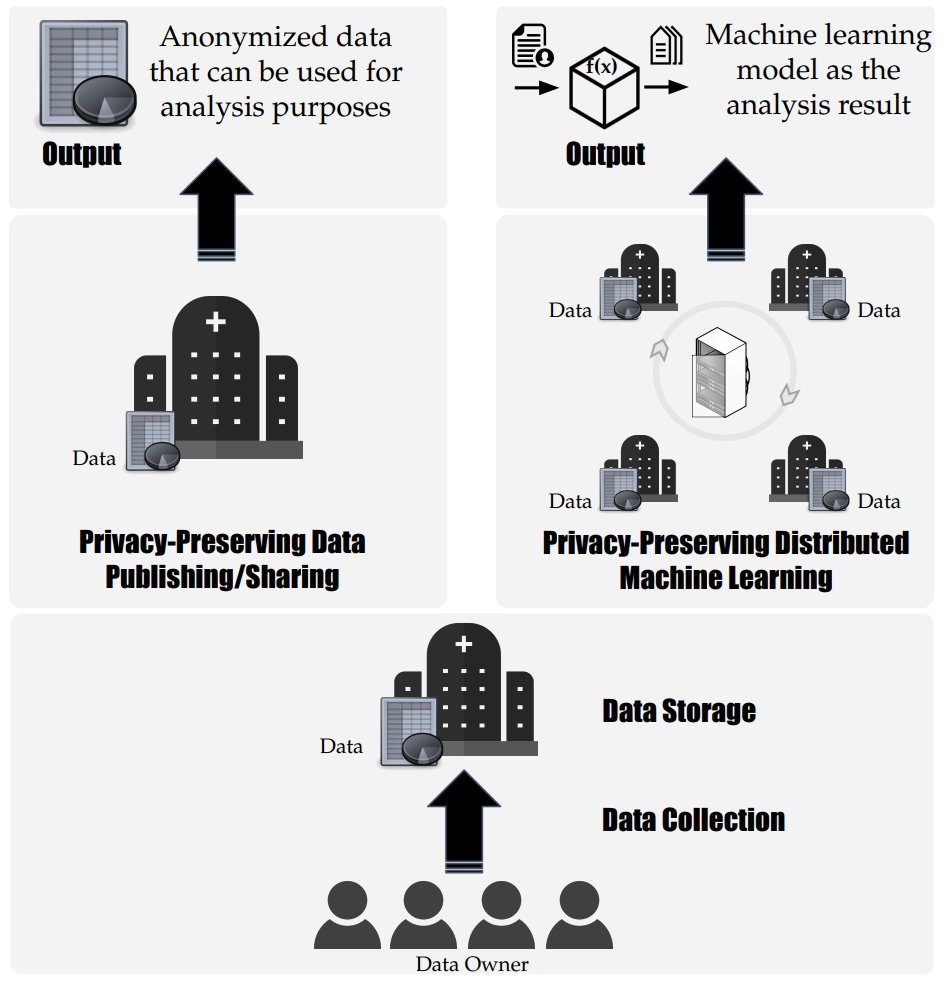
Graphical abstract
Abstract
Artificial intelligence (AI) and automated decision-making have the potential to improve accuracy and efficiency in healthcare applications. In particular, AI is proved to outperform human experts in certain domains. However, the application of AI and machine learning for automated decision-making in healthcare comes with challenges, such as security and privacy preservation. Such issues are among the primary concerns that must be addressed as they may negatively affect individuals. For instance, a patient’s privacy is violated if sharing his/her medical data with a third-party data recipient reveals that he/she had a medical condition. Furthermore, particular guidelines, e.g., General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), are proposed to legally protect the privacy of patients that has to be observed while employing AI and machine learning in this domain.
In order to address such privacy concerns, in this thesis, we consider two principal directions for the analysis of data and concentrate our research on them. In one primary direction, the analysis is performed on the published/shared data. Therefore, the data holder needs to consider particular measures to protect the privacy of data subjects, for instance, by perturbing the data before publishing. In this thesis, along this direction, we propose an anonymization framework, formulated as an optimization problem, for datasets with both categorical and numerical attributes. The proposed framework is based on clustering the data samples by considering the diversity issue in anonymization to reduce the risks of identity and attribute linkage attacks. Our method achieves anonymity by formulating and solving this problem as a constrained optimization problem, by jointly considering the k-anonymity, l-diversity, and t-closeness privacy models. We evaluate our framework on popular publicly available structured healthcare data.
The other primary direction is to perform analysis without publishing the data. In such settings, we consider multiple parties, each of which holds a different part of the data. The objective is to analyze the data held on these parties without direct access to the data record values. In this thesis, along this direction, we present a scalable privacypreserving distributed learning framework based on the Extremely Randomized Trees (ERT) algorithm and Secure Multiparty Computation (SMC) techniques. We build a machine learning model based on the entire dataset by analyzing the data locally at each party and combining the results of this analysis. We evaluate the distributed implementation of our technique based on healthcare datasets collected in the INTROMAT project and demonstrate its prediction performance.
In summary, the research in this thesis contributes to the possibility of exploiting health data in the healthcare setting for analysis and automatic decision-making without privacy violation. This has a long-term potential for better decision-making in the healthcare context, diagnosis, and treatment, at an affordable cost.
BibTeX
@misc{aminifar2022privacy,
title={Privacy-Preserving Machine Learning and Data Sharing in Healthcare Applications},
author={Aminifar, Amin},
year={2022},
publisher={H{\o}gskulen p{\aa} Vestlandet}
}