RecogNoise: Machine-Learning-Based Recognition of Noisy Segments in Electrocardiogram Signals
![]() Download PDF
Download PDF
![]() Citation
Citation
![]() Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Graphical abstract
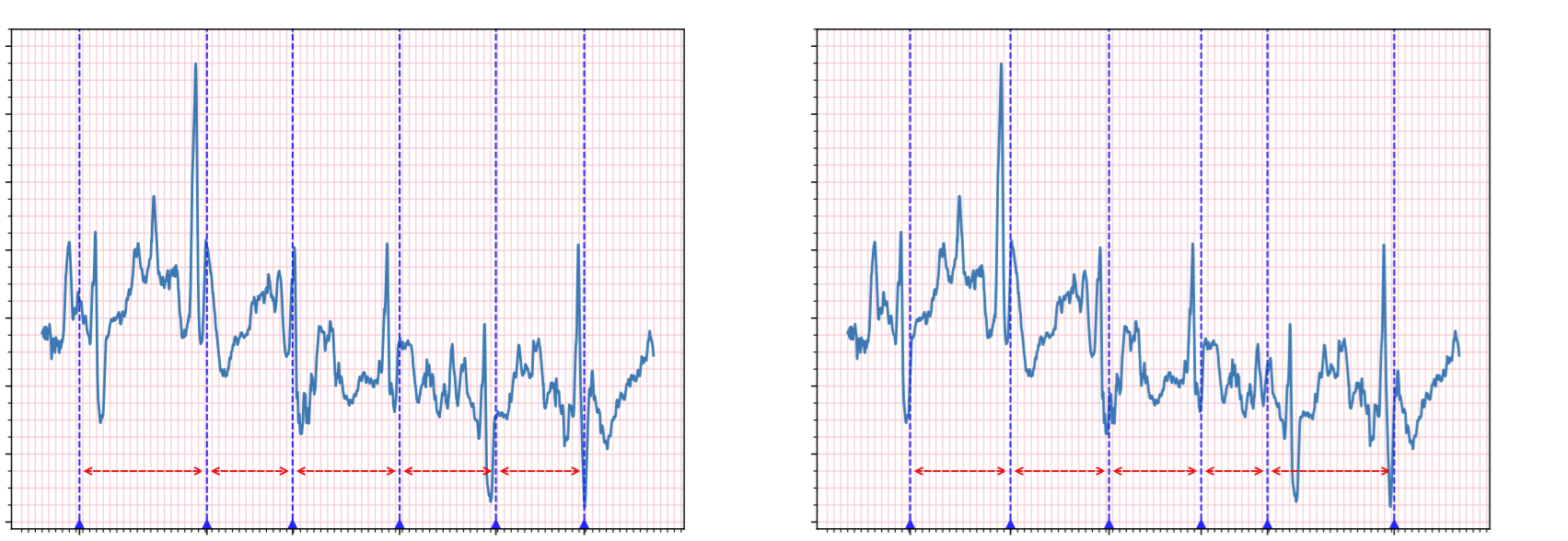
Abstract
Today, wearable technology is frequently used for continuous monitoring of physiological indicators in the health-care domain. However, mobile-health and wearable devices are generally used in ambulatory settings, hence vulnerable to noise. This interferes with the accuracy of Machine Learning (ML) models running on such systems and their decision-making procedures. To address this issue, we first need to identify the presence of noise. In this paper, we propose RecogNoise to detect noisy segments in Electrocardiography (ECG) recordings using heartbeat detection algorithms and ML. We evaluate our approach based on the MIT-BIH arrhythmia database and three types of noise, i.e., Electrode Motion (EM) , Baseline Wander (BW), and Muscle Artifact (MA), with different Signal to Noise Ratios (SNRs). We show that RecogNoise can detect noisy segments with an F1-score of 86.9% and an accuracy of 88.3%.
BibTeX
@inproceedings{aminifar2024recognoise,
title={Recognoise: Machine-learning-based recognition of noisy segments in electrocardiogram signals},
author={Aminifar, Amin and Khooyooz, Soheil and Jahanjoo, Anice and Shakibhamedan, Salar and TaheriNejad, Nima},
booktitle={2024 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS)},
pages={1--5},
year={2024},
organization={IEEE}
}